LinkedIn Impersonated in Identity Theft Scheme
In a recent attack uncovered by Abnormal Security, the attacker impersonates LinkedIn to send a malicious attachment that could lead to identity theft. Once the attachment is opened, the victim is asked to put in personal identifying information, including their social security number.
January 27, 2021

In a recent attack uncovered by Abnormal Security, the attacker impersonates LinkedIn to send a malicious attachment that could lead to identity theft. Once the attachment is opened, the victim is asked to put in personal identifying information, including their social security number.
Summary of Attack Target
Abnormal Security first observed this attack targeting one of our customers.
- Platform: Office 365
- Victims: Executives and VIPs
- Payload: Malicious Attachment
- Technique: Name Impersonation
LinkedIn Impersonated in Original Attack
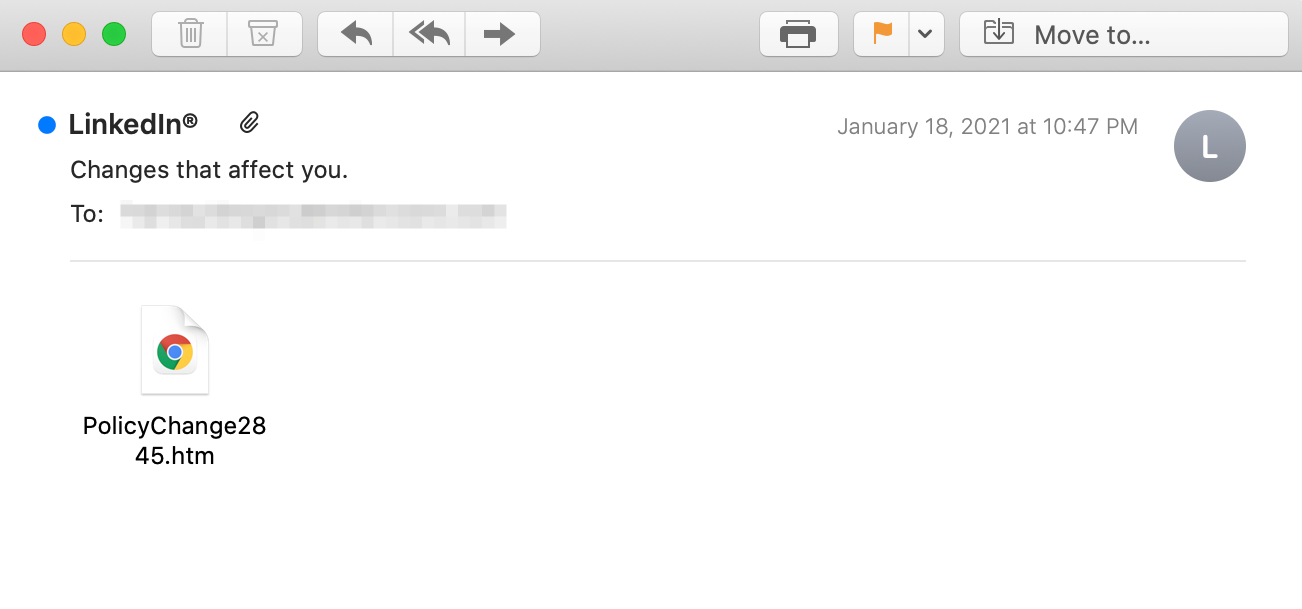
In this attack, the recipient receives an email from what appears to be LinkedIn, at least according to the display name. The email contains only an HTM attachment named “PolicyChange2845,” prompting the recipient to open the file. At first glance, the recipient may think that this is a policy change notification coming from LinkedIn. The email subject states “Changes that affect you,” increasing the urgency to open the attachment.
However, when taking a closer look, we can see that while the display name is LinkedIn, the actual sending email address is ‘policychange@fzx.com,’ which has no relation to LinkedIn. The attacker is using name impersonation in hopes of deceiving the recipient.
When opening the attachment, the recipient is asked to complete a form that looks similar to the LinkedIn login or sign-up page. This form contains boxes to input the recipient’s name, social security number, date of birth, and driver’s license number. Meanwhile, the legitimate LinkedIn site would only ask for an email and password to login.

If the recipient of this email falls victim to this attack and fills out the form they are prompted with, they will have released extremely sensitive information to the attacker. The attacker would not only have their name and date of birth, but also their social security number and driver’s license information—all of which can quickly lead to identity theft.
Why This Attack Bypassed Traditional Security
Because this attack does not contain a traditionally malicious attachment, it would likely bypass a secure email gateway that would look for malware hidden within the attachment. Instead, this attack uses urgency and credential phishing to encourage someone to open the attachment and complete the form.
By understanding identity and impersonation, Abnormal Security is able to detect the nature of the message and understands that it is likely dangerous—despite not containing malicious code. Further analysis of the text within the email also indicates that the body contains text and spaces with a size zero font, a common pattern that we've observed in email attacks.
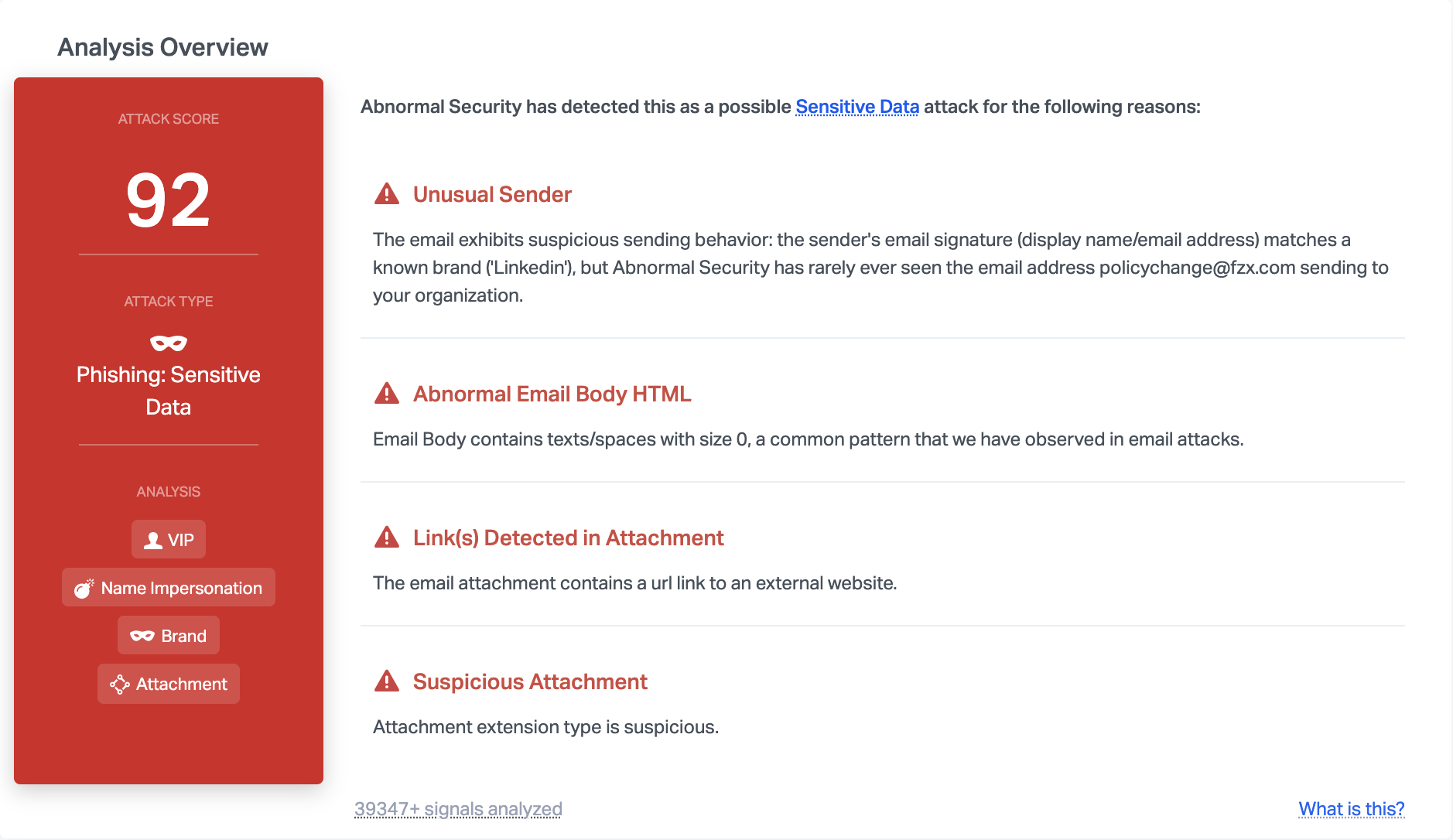
Taken together, Abnormal has enough signals to mark this email as an attack, and prevent it from reaching end users.
Related Posts
Get the Latest Email Security Insights
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive updates on the latest attacks and new trends in the email threat landscape.