Beyond the Firewall: Why Watering Hole Attacks Demand Behavioral Detection
Learn how watering hole attacks work and how to stop them with AI-powered detection and behavioral analysis.
May 22, 2025
Watering hole attacks turn trusted websites into entry points for cyber threats. Instead of targeting individuals directly, attackers compromise sites your employees already visit and quietly insert malicious code to reach their true targets.
These attacks are precise, hard to detect, and increasingly used in sophisticated threat campaigns. But even if the initial compromise goes unnoticed, the behavior that follows doesn’t have to.
With behavioral analysis and AI-powered detection, security teams can stop watering hole attacks before they escalate, protecting users without disrupting productivity.
What Is a Watering Hole Attack?
A watering hole attack is a targeted cyberattack where threat actors compromise a website commonly visited by their intended victims. Rather than reaching out to users directly, attackers wait for them to come to a trusted site, then silently deliver malware or exploit browser vulnerabilities.
The name comes from the predator-prey analogy: just as predators wait at a watering hole for prey to appear, attackers stake out digital “watering holes” like industry blogs, vendor portals, or internal web apps. These attacks are designed for stealth and precision, often used by advanced persistent threat (APT) groups in espionage or supply chain campaigns.
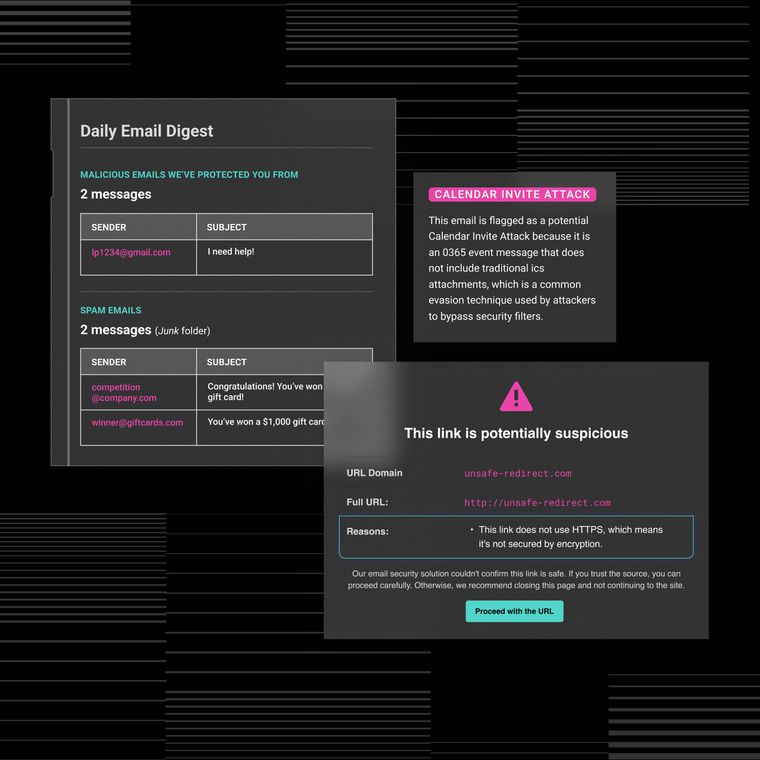
Watering hole attacks are dangerous because they start in places users already trust. That trust makes traditional security tools, like email filters or endpoint protection, less effective on their own. Without behavioral visibility, the breach can go unnoticed until it escalates into credential theft, lateral movement, or even business email compromise.
That’s why forward-thinking security teams rely on AI-driven detection and behavioral analysis to catch anomalies early, even when the entry point happens outside the organization’s perimeter.
How Does a Watering Hole Attack Work?
Watering hole attacks follow a deliberate sequence, from reconnaissance to exploitation.
They typically use an indirect approach that bypasses perimeter defenses by turning trusted websites into silent delivery mechanisms. That’s why behavior-based detection is essential. Even if the initial access point is invisible, the attacker’s next move won’t be.
Here’s how watering hole attacks typically unfold:
Identify the Target’s Habits: Attackers profile their victims to find out which websites they frequently visit, like partner portals, vendor dashboards, or niche industry resources.
Compromise a Trusted Site: Using stolen credentials or exploiting vulnerabilities, attackers gain access to the backend of a legitimate site that the target trusts.
Inject Malicious Code: They embed hidden code, usually a script or iframe, that executes automatically when the page loads, without disrupting the user experience.
Deliver the Payload: If the visitor’s system is vulnerable, malware is silently installed to enable access, surveillance, or lateral movement.
Because these attacks start outside your perimeter, they often evade traditional defenses. Behavioral detection catches what static tools miss—identifying abnormal activity after the compromise, before it becomes a breach.
This type of strategic website compromise shares similarities with other advanced techniques like drive-by downloads, where malicious code executes without user interaction. Attackers often exploit zero-day vulnerabilities and social engineering to gain a foothold in the network.
Why Traditional Defenses Often Miss These Attacks
Most legacy tools like antiviruses, firewalls, and secure email gateways (SEGs) were built to stop malware, not manipulation. They rely on threat signatures and known bad behavior, which simply don’t apply to many of today’s most dangerous email attacks.
Threat actors now use social engineering tactics over software exploits. Attacks are often payload-less, sent from trusted identities, and crafted to blend in with routine business communication. These tactics bypass filters that expect links or attachments as proof of risk.
Even reputation-based tools fall short. Attackers host phishing pages on services like SharePoint or Google Drive. Because these domains are considered safe, traditional systems let them through, no matter what’s waiting on the other side.
In other words, the limitations of traditional defenses mean that:
They’re built to block malware, not manipulation.
They trust known-good services, even when attackers exploit them.
They lack context around identity, tone, and communication patterns.
To defend against today’s threats, organizations need adaptive detection strategies. These solutions establish baselines for normal activity, then surface deviations that signal risk, even in messages that appear legitimate.
How Behavioral Detection Can Spot Anomalies After the Initial Compromise
After an attacker gains access to a Microsoft 365 account, their behavior almost always deviates from the norm. Behavioral detection identifies those deviations by analyzing identity, content, and context over time.
Modern security tools like Abnormal use behavioral AI to establish a unique behavioral baseline for every user in your environment. When activity falls outside that baseline, that activity is flagged, regardless of whether credentials were valid or the login looked legitimate.
It detects post-compromise activity such as:
Unfamiliar Communication Patterns: Emails sent to new recipients, unusual distribution lists, or mass messaging behavior that doesn’t match the user’s normal cadence.
Anomalous Content or Tone: Language that’s overly urgent, transactional, or inconsistent with how the user typically writes.
Unexpected Access Behaviors: Logins from unusual locations, devices, or at hours outside the user’s normal activity window.
Inbox or Configuration Changes: Forwarding rules, MFA bypass attempts, or permission escalations that weren’t made through official channels.
Lateral Movement Signals: Internal phishing, privilege testing, or attempts to compromise additional accounts.
Implementing effective identity defense strategies is essential for detecting deviations in user behavior. These signals often go unnoticed by traditional tools that focus on static indicators. Abnormal uses behavioral AI to continuously assess user activity, making it possible to detect and remediate threats even after an attacker is inside.
Even when the initial compromise succeeds, the attack doesn't need to.
How to Reduce Organizational Risk From Watering Hole Attacks
While watering hole attacks are hard to prevent at the source, organizations can reduce risk by focusing on preparation, segmentation, and post-compromise detection.
Train Users to Recognize Behavioral Red Flags
Most users won’t know a website has been compromised, but they can still spot unusual follow-up behavior.
Train teams to escalate unexpected login prompts, system slowdowns, or file access anomalies. Security awareness programs should educate users on how to spot phishing emails and include watering hole scenarios as part of broader phishing and social engineering training to combat manipulation-based attacks.
Enforce Least Privilege Access
Minimize the impact of compromise by limiting lateral movement. Enforce strict access controls so users only have permissions essential to their role. If a device is infected through a browser exploit, this containment strategy reduces the attack surface.
Evaluate Vendor and Third-Party Website Risk
Audit your critical third-party vendors regularly. Require them to share vulnerability reports, software update cadences, and security certifications. Use tools to scan their web presence for outdated CMS versions or exposed admin panels, and flag domains that show signs of compromise or recent defacement. Ensure vendor risk assessments are documented and reviewed quarterly.
Detect Abnormal Behavior After Compromise
Use behavioral AI to monitor user and system activity continuously. Flag logins from unusual locations, unexpected privilege escalations, and communication with unknown domains. Integrate this monitoring into your incident response process so alerts immediately trigger investigation workflows.
Stop Email-Based Threat Escalation
Watering hole attacks often open the door to downstream threats like internal phishing or executive impersonation. Using advanced detection methods, Abnormal detects shifts in email behavior, like sudden changes in tone, unusual recipient lists, or suspicious financial requests, and blocks attacks before they spread. Make this part of your layered defense strategy to reduce downstream risk.
The Bigger Picture: Watering Hole Attacks and the Modern Supply Chain Threat Landscape
Watering hole attacks are a part of a larger trend of supply chain compromise, where attackers exploit the trust placed in third-party vendors and shared infrastructure. These targeted attacks blur the line between external compromise and internal threat, making it harder to detect breaches using perimeter-based tools alone.
That’s why behavioral AI matters. By understanding what normal looks like for every user and vendor, Abnormal surfaces anomalies early, before attackers can escalate access or move laterally via email.
Explore how Abnormal protects against modern supply chain threats with behavioral AI and post-compromise visibility built for today’s attack surface.
Related Posts
Get the Latest Email Security Insights
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive updates on the latest attacks and new trends in the email threat landscape.