Training Best Practices That Improve Fake Emails Recognition
Boost recognition of fake emails with training best practices that strengthen phishing awareness.
October 26, 2025
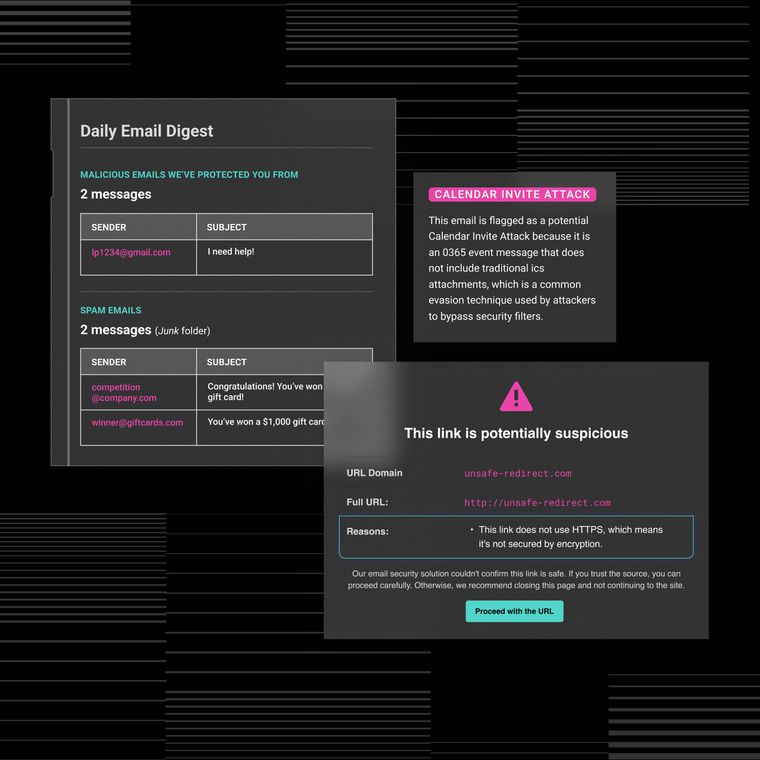
Smart employees click phishing links because modern attacks mirror legitimate business communications with surgical precision. In fact, the attackers research your organizational chart, clone executive email addresses, and reference active projects to extract personal information or authorize fraudulent transfers. Professional writing has replaced obvious typos, while messages arrive during peak workload hours when cognitive defenses are weakened.
That said, generic red-flag training won't suffice against these sophisticated threats. An effective phishing training program to improve fake email detection requires the following eight specific practices that also lay the foundation for AI-powered email security.
1. Start with Real Attack Examples Your Industry Actually Faces
Employees learn fastest when they dissect genuine scams from their actual inbox, not textbook screenshots. Use sanitized emails that reference your real vendors, workflows, and executive titles. Attackers already conduct this reconnaissance, so your training must expose it.
Pull templates from curated libraries of actual phishing attempts or industry-specific breaches. Rotate new samples monthly to keep content fresh and contextually relevant, as detection rates climb with current examples. After each walkthrough, break down which social engineering trigger drove clicks, like urgency, authority, or reward. This authenticity createsa lasting memory that translates directly to faster real-world recognition.
2. Create Department-Specific Training That Matches Daily Work Reality
Generic "spot the red flags" lessons leave critical gaps. Finance teams need practice spotting payment-redirect scams, while HR must distinguish malicious résumés from legitimate attachments. Role-specific simulations boost detection rates more than generic drills by addressing each team's unique vulnerabilities.
Build scenarios that mimic actual software and jargon, such as an IT help-desk ticket with technical abbreviations, or a sales inquiry referencing current pricing. Tailor difficulty to each group's access level and risk: executives see sophisticated business email compromise attempts; interns get foundational exercises. By mapping threats to real responsibilities, you transform abstract guidance into muscle memory that employees apply without hesitation.
3. Focus on Context and Timing Instead of Just Technical Red Flags
Attackers strike when you're rushing to close the quarter or checking email during holiday travel. Research shows susceptibility spikes during busy periods and declines after targeted refreshers. Teach employees to pause when an unexpected request lands outside normal hours or when a message bypasses the usual approval chain.
Encourage verification of high-stakes asks through a second channel. For instance, call the requester on a known number instead of replying. Reinforce this habit with simulations delivered at random, high-stress moments, so people practice slowing down when they feel pressure. This timing awareness moves vigilance from "check the link" to "check the situation."
4. Make Reporting Easy and Rewarding Instead of Punitive
Employees hesitate to report fake-looking emails when the process feels complicated or punitive. Deploy a one-click "Report Phish" button in every mailbox with instant confirmation so users know their alert reached security teams. This is because clarity and psychological safety significantly increase reporting volume.
Recognize departments that identify real attacks, and never penalize employees who click before reporting. Fear suppresses honest disclosure, creating blind spots that attackers exploit. Additionally, pair increased reporting with automated triage workflows that eliminate duplicates and route enriched headers to security platforms. Without intelligent filtering, high reporting volumes overwhelm analysts and slow response times.
When reporting feels straightforward and consequence-free, organizations gain thousands of human threat sensors who actively strengthen defenses rather than avoiding involvement.
5. Use Interactive Simulations That Feel Like Real Work Situations
Static slide decks fail to create lasting behavioral change. Deploy interactive phishing simulations during business hours to deliver visceral lessons that employees remember under pressure. Send regular, tailored exercises to staff, adjusting complexity based on individual performance metrics and organizational risk profiles.
Design each simulation around authentic business decisions like approving invoices, sharing documents, or booking travel. These realistic scenarios mirror daily workflows, making recognition patterns transferable to actual threats.
When employees engage with simulated attacks, deliver immediate micro-training that identifies the specific indicators they missed and reinforces proper reporting procedures. This adaptive approach challenges high performers with sophisticated scenarios while providing targeted support for struggling team members, maintaining security awareness without disrupting productivity.
6. Train Recognition of Subtle Social Engineering Tactics
Modern phishing often omits the misspellings and sketchy links your old training warned about. Attackers hijack existing threads, reference recent product launches, or cultivate rapport over the course of weeks. Walk employees through these psychological levers. Show how a fake Zoom invite exploits urgency, or how a gift-card fake email taps into reward bias.
Emphasize that tone, context, and behavioral cues matter as much as technical markers. By naming the emotion being manipulated, you give people a meta-alert that something feels off, transforming abstract awareness into practical defense skills.
7. Build Organizational Habits Around Verification and Double-Checking
Security culture sticks when verification becomes routine, not a special event. Set clear thresholds, such as making it mandatory for any payment above a set amount to require voice confirmation on a published phone number. Or, publish workflows that require a second approver for sensitive data pulls.
Reinforce these habits with scenario training. An urgent wire request that bypasses finance, or a benefits form asking for Social Security numbers. Employees who practice the call-back or chat-back step in training will repeat it instinctively when real pressure hits. Over time, verification shifts from an extra chore to the standard way business processes operate.
8. Measure What Matters and Continuously Improve Training Effectiveness
Click rates alone tell you who got fooled, not who saved the day. Track the percentage of suspicious emails employees report, the median time from delivery to first alert, and how many real attacks you prevented. Pair these metrics with periodic confidence surveys to spot gaps before they become incidents.
Baseline tests identify persistent outliers who need extra coaching, while longitudinal data shows whether refreshers are spaced correctly. Feed these insights into your AI email security platform so it learns from human vigilance and sharpens automated detection.
When Training Meets Its Natural Limits
Even highly trained employees struggle with sophisticated phishing attacks that exploit legitimate business relationships, using authentic grammar, branding, and context that blur the lines between real and fake. These attacks capitalize on cognitive biases while overwhelming staff with the impossible task of scrutinizing every email for potential threats.
AI provides consistent vigilance beyond human capacity, analyzing behavioral patterns specific to your organization. This technology continuously analyzes anomalies in email behavior, delivering protection against threats without the fatigue that human defenders experience.
Integrating AI into your defense strategy complements human training rather than replacing it. Humans bring intuition and contextual understanding, while AI delivers relentless analysis that identifies subtle discrepancies across massive data sets. This combined approach balances human insight with technological precision, fortifying email security against increasingly sophisticated phishing attempts.
Organizations seeking this combined defense can leverage behavioral AI platforms that learn unique communication patterns and adapt to emerging threats. Discover how Abnormal's AI-powered email security strengthens your human-centered training program with continuous, intelligent threat detection. Book a personalized demo today.
Related Posts
Get the Latest Email Security Insights
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive updates on the latest attacks and new trends in the email threat landscape.