Why Legacy Email Spam Filtering Misses Identity-Based Attacks (and How to Evolve)
Learn why legacy spam filtering misses identity-based attacks and how evolving email security can stop them.
October 1, 2025
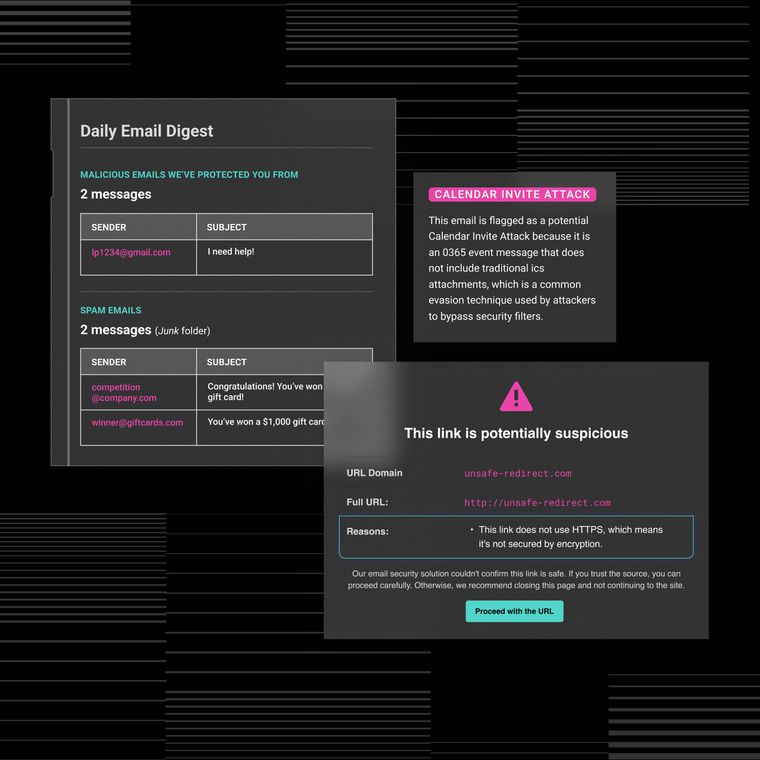
Legacy spam filters fail against identity-based email attacks because they were designed to stop bulk spam, not targeted threats that exploit human psychology and trust relationships. Business email compromise (BEC) scams inflicted $2.7 billion in losses during 2023, with attackers succeeding by convincing users to click on phishing links or surrender personal information, rather than deploying malicious code.
These sophisticated attacks bypass outdated filters that cannot evaluate sender intent, relationship context, or subtle changes in communication patterns. Modern threats require a fundamentally different approach, one that understands behavior, context, and the human element that traditional security tools often overlook. Let’s understand some reasons why legacy email spam filtering misses identity-based attacks.
1. Built for Volume, Not Precision
Legacy spam filters excel against mass email campaigns but fail against targeted identity attacks because they rely on static rules rather than behavioral analysis. Traditional filtering systems depend on keyword blacklists, sender reputation scores, and bulk-mail detection patterns that sophisticated attackers easily circumvent using everyday business language and compromised legitimate accounts.
Rule-based systems scan for surface indicators. These include specific keywords, known malicious domains, and volume patterns associated with spam campaigns. These tools treat each email in isolation, missing the contextual relationships and communication patterns that reveal identity-based threats. When attackers craft messages using normal business vocabulary from newly created domains or compromised accounts, traditional filters often fail to detect anything suspicious.
Additionally, modern behavioral AI examines contextual cues and established baselines of normal behavior rather than relying on static indicators. This sophisticated analysis identifies subtle differences in communication patterns, timing anomalies, and relationship dynamics that traditional filters ignore entirely, enabling detection of threats that perfectly mimic legitimate business correspondence.
While legacy filters require manual updates to address new threat patterns, behavioral AI continuously learns from live traffic, automatically adjusting detection parameters as attack techniques evolve. This dynamic approach ensures protection against zero-day identity attacks that exploit previously unknown vulnerabilities or social engineering tactics.
2. Blind to Behavioral Anomalies
Legacy tools lack the organizational context needed to detect subtle anomalies in sender behavior, treating each email as an isolated event rather than part of ongoing communication patterns. This blindness to behavioral context allows identity-based threats to slip through undetected.
Behavioral baselining establishes standards of normal operations and communication patterns for every user and vendor relationship. The system identifies anomalies, including unusual communication timing, shifts in writing style or tone, and requests that deviate from established patterns. For example, an attacker might alter banking details in a vendor invoice that passes DMARC checks but deviates from usual language patterns: a change invisible to legacy systems but immediately flagged by behavioral analysis.
Behavioral AI simultaneously analyzes sender history, recipient relationships, content semantics, and timing patterns to build comprehensive risk profiles. This multidimensional analysis reveals sophisticated attacks that align with some normal parameters while deviating in others, such as correct sender domains but unusual request patterns.
Unlike legacy filters that process emails without historical context, behavioral AI maintains institutional knowledge of communication patterns, vendor relationships, and business workflows. This organizational memory enables the detection of subtle deviations that indicate compromise, such as a trusted vendor suddenly requesting payment to a new account.
3. Missing the Human Layer of Exploitation
Identity-based attacks weaponize urgency, authority, and familiarity. These include psychological elements that content filters cannot assess effectively. These attacks succeed by manipulating human psychology rather than exploiting technical vulnerabilities.
Social engineering techniques frequently employed include authority fraud, where imposters demand immediate wire transfers claiming CEO authorization. Urgency tactics transform routine requests into emergencies through phrases like "critical deadline" or "immediate action required." Familiarity spoofing hijacks genuine conversation threads, continuing previous discussions to establish trust before introducing malicious requests.
Business Email Compromise attacks succeed primarily because traditional methods cannot scale efficiently against psychological manipulation. Signatures lack predictive capability for novel social engineering tactics, while the human eye cannot process the volume of emails necessary to identify subtle manipulation patterns. These attacks bypass conventional filters because they contain no malicious payloads; instead, they rely on psychological triggers that traditional systems cannot evaluate.
By mapping organizational relationships and communication patterns, behavioral AI identifies when requests violate established hierarchies or bypass normal approval channels. This relationship intelligence catches impersonation attempts that use correct names and titles but originate from unauthorized sources.
4. Ineffective Against Compromised Accounts
Emails from compromised accounts bypass legacy anti-spam measures, including SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, because these protocols verify domain ownership without assessing sender intent or behavioral context. Authentication protocols provide binary pass/fail verification, confirming domain legitimacy without behavioral analysis.
Consider a compromised CFO account requesting urgent wire transfers: the email passes authentication, uses proper formatting, and originates from the correct domain, yet represents a serious security threat.
Behavioral AI performs risk scoring by analyzing communication patterns, access behaviors, and content anomalies that traditional authentication protocols often overlook. The system detects when legitimate accounts start behaving differently. These include accessing systems from new locations, sending messages at unusual times, or making requests outside normal patterns.
Generative AI enables attackers to craft flawless, context-aware messages that static filters cannot detect. Attackers leverage LLMs for automated reconnaissance using public data, creating convincing voice deepfakes for follow-up calls, and crafting highly personalized phishing messages that reference real projects and mirror organizational communication styles.
Behavioral AI offers continuous model retraining on live traffic patterns, allowing real-time adaptation to emerging threat techniques. Cross-channel correlation identifies coordinated campaigns spanning email, collaboration platforms, and voice channels. Only AI can effectively combat AI-powered threats at scale, providing the computational power and pattern recognition necessary to identify machine-generated attacks. This AI-versus-AI paradigm represents the new reality of email security.
Move Beyond Spam Filtering with Behavioral AI
Behavioral AI overcomes legacy gaps by modeling relationships, context, and intent across all communication channels. This approach establishes baselines of normal behavior for individuals and vendors, flagging anomalies that indicate potential compromise or fraud.
Modern behavioral AI solutions follow a four-step framework, which includes an API-based cloud data ingestion for seamless integration; baseline establishment and mapping of normal user, vendor, and application behavior; machine learning models identifying threats through pattern deviation; and automated remediation, providing contextual responses or direct protective actions.
Organizations implementing behavioral AI report significant reduction in false positives, protection deployed within minutes versus months, and unified coverage across email, Slack, Teams, and Zoom. Security teams experience significant workload reductions as automated analysis handles routine investigations.
There's a reason why organizations are moving beyond traditional spam filtering to address identity-based attack challenges. Ready to strengthen your email security with AI-driven behavioral analysis? Get a demo to see how Abnormal can protect your organization from sophisticated threats that legacy filters miss.
Related Posts
Get the Latest Email Security Insights
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive updates on the latest attacks and new trends in the email threat landscape.