Top 3 Ways Security Frameworks Help Prevent Phishing Attacks
Use proven frameworks to build phishing-resistant systems, policies, and user training.
July 29, 2025
Phishing attacks continue to evade traditional defenses, resulting in billions of dollars in annual losses. Business email compromise (BEC) alone accounted for $2.77 billion in losses last year. Modern phishing tactics, ranging from AI-generated emails to vendor impersonation, demand more than reactive tools. Security frameworks, such as NIST CSF, CIS Controls, and Zero Trust, offer structured, proactive approaches to prevent these threats from reaching users.
The Problem: Phishing Outsmarts Traditional Defenses
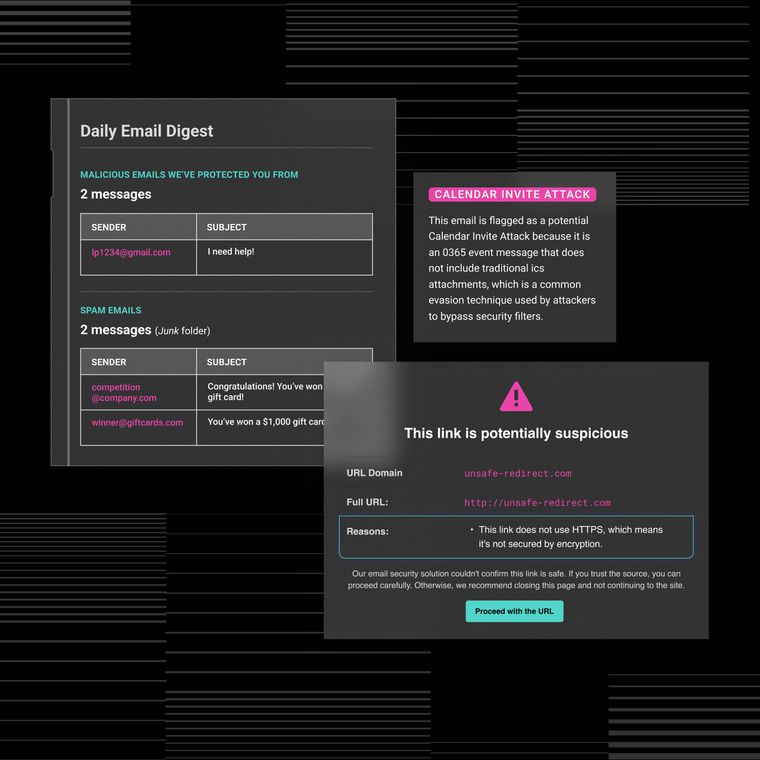
Legacy email defenses often fail against modern phishing because they rely on static filters, while attackers use dynamic, trusted methods. Secure Email Gateways miss novel, text-based emails sent from authenticated domains, leaving gaps for attackers to exploit.
Phishing campaigns now mimic trusted vendors, complete with accurate branding, thread history, and valid SPF/DKIM, making fake requests nearly indistinguishable. AI-generated messages further bypass content-based filters by imitating real corporate communication.
User training helps but doesn’t scale. Organizations need framework-aligned policies and behavioral AI that detects anomalies in communication to stop phishing before damage occurs. Let’s understand the three ways security frameworks help prevent phishing attacks:
1. Establish Robust Email Policies and Controls
Security frameworks like NIST, CIS Controls, and Zero Trust emphasize the need for structured email policies to reduce exposure and stop threats before they reach inboxes.
Begin with core controls. NIST SP 800-53 outlines protections for email at the network and transmission levels (SC-7, SC-8), while CIS Control 9 focuses on secure email and browser configurations. Translate these into concrete actions with technical safeguards.
Start by enforcing strong email authentication. Configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC with a reject policy to block spoofed emails. Track the percentage of protected domains to gauge coverage and highlight gaps.
Strengthen access control with phishing-resistant MFA across all accounts. Use FIDO2 tokens or WebAuthn keys, especially for users with privileged access. These methods eliminate credential phishing risk by preventing replay attacks.
Apply least-privilege principles by separating administrative email accounts from everyday use and limiting who can modify mail flow rules. Implement continuous monitoring to detect unusual activity across all email infrastructure, aligned with NIST CSF Detect and CIS Control 8.
Zero Trust and NIST both stress the importance of verifying user identity and device posture for every session. Enforce authentication, authorization, and risk evaluation for every message interaction.
To measure effectiveness, track:
DMARC reject adoption across all owned domains
MFA enrollment across all users (aim for 100 percent)
Privileged mailbox hardening, including role separation and continuous monitoring
As these metrics improve, spoofed messages get blocked, credential theft fails, and attackers lose access to high-value inboxes. These outcomes reflect Zero Trust principles and demonstrate that policy-driven email security is actively preventing phishing threats.
2. Promote User Awareness and Response Protocols
Security frameworks consistently highlight the importance of user awareness and structured response plans in defending against phishing. NIST 800-50 and ISO 27002 emphasize the importance of security education, while the NIST CSF associates awareness with the Protect function and incident response with the Respond function. CIS Control 14 links both through clear, measurable actions.
Build your program around continuous, role-based education. Supplement it with frequent simulations and just-in-time micro-training. Embed a “Report Phish” button in email clients to make user reporting seamless. Organizations that combine simulations with contextual feedback consistently reduce click rates and increase reporting accuracy.
Focus training on practical red flags:
Encourage employees to hover over links before clicking and examine destination URLs.
Teach users to verify email addresses against known contacts, especially for financial or sensitive requests.
Reinforce the need to pause and investigate when messages demand urgency or secrecy.
Gamified learning boosts engagement. Offer micro-rewards for accurate reporting and rapid response to phishing simulations. Reinforce lessons with instant feedback after each test to build long-term awareness.
Awareness must be paired with clear next steps. Response protocols should include guidance on how to report suspected phishing, isolate threats, and trigger automated containment through tools and playbooks aligned with NIST CSF Respond.
Measure impact consistently. Key metrics include reporting rates, click-through reduction, repeat-offender trends, and mean time to contain incidents. Use these insights to refine training, target retraining efforts, and prove program effectiveness.
When users are trained, empowered, and supported by well-defined response procedures, they become an extension of your security posture, feeding intelligence into monitoring systems and helping stop threats before they escalate.
3. Enable Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Continuous monitoring and real-time threat intelligence are foundational to modern security frameworks. NIST, CIS Controls, and Zero Trust all emphasize the importance of ongoing visibility into user activity, email traffic, and identity access.
To implement this, organizations must centralize telemetry from email systems, SaaS platforms, endpoints, and identity providers. Behavioral analytics then detect anomalies, like a sudden vendor payment request or a user clicking a suspicious link late at night. SIEM platforms normalize events, while SOAR tools trigger automated responses such as quarantining emails, resetting passwords, or revoking access tokens.
The process should be tightly integrated, encompassing the steps of collecting, analyzing, detecting, alerting, and responding. Automation at each step is critical as manual triage cannot keep pace with the speed and complexity of today’s phishing attacks.
Threat intelligence further enhances monitoring by enriching events with indicators like domain reputation or newly registered look-alike domains. Vendor risk tools extend this insight, flagging compromised partners before malicious activity reaches your team.
Effective programs measure results. Key metrics include mean time to detect, anomaly resolution rates, and the percentage of external data sources actively ingested. Organizations that automate detection and response significantly reduce dwell time and prevent credential misuse.
When combined with behavior-based protection, continuous monitoring becomes a live defense system, proactively stopping threats before they escalate into breaches.
Frameworks Lay the Groundwork and Abnormal AI Elevates Protection
Security frameworks provide critical structure for email protection, but advanced phishing attacks often slip past static defenses. Abnormal strengthens these defenses with behavioral AI that understands how your organization truly communicates.
By integrating via API, Abnormal analyzes every message to build a comprehensive behavioral profile of users, including their communication patterns and intent. When an email deviates from normal behavior, even if it appears legitimate, Abnormal flags and isolates the threat in real time.
This intelligent, adaptive approach reduces breaches, alleviates alert fatigue, and accelerates investigations. Request a demo to see how Abnormal’s behavioral AI enhances your security framework with precision threat detection.
Related Posts
Get the Latest Email Security Insights
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive updates on the latest attacks and new trends in the email threat landscape.